How the Metaverse Is Energizing Media and Entertainment
The media and entertainment (M&E) industry has chalked up several metaverse firsts. Enterprises cast the usual suspects to produce immersive experiences: virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), artificial intelligence (AI), internet of things (IoT), non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and blockchain. However, a capability required for a full-blown metaverse – near-zero latency delivered by 5G, data centers and edge computing – isn’t yet available. In the meantime, latency is low enough for enterprises to deliver certain metaverse experiences. Both the M&E and data center industries, along with companies that have or want to have skin in the game, are forging ahead.
How is the metaverse energizing M&E? Consider the examples below, along with comments on the future of the metaverse and the infrastructure that runs it behind the scenes.
The Metaverse, Whatever It Is, Generates Lots of Buzz
Industry watchers, investors and product companies each put forth their vision of the metaverse. A lack of consensus doesn’t seem to dampen momentum. TechCrunch’s recent M&E/metaverse headlines reflect the positive and negative views typical of many emerging technologies:
- Metaverse is just VR, admits Meta, as it lobbies against ‘arbitrary’ network fee
- Roblox to host a free virtual Super Bowl concert featuring Sweetie
- I actually had fun at Fatboy Slim’s metaverse rave
- Disney cuts metaverse division as part of broader restructuring
- A decade later, this VR treadmill is finally ready to ship
Headlines aside, immersive experiences are on the rise. Fortnite hosted Marshmello in what’s called the first virtual concert, in early 2019. During the follow-on Travis Scott concerts in 2020, 27.7 million concurrent players participated live.1 Other notable examples:
- Illuvium, a new video game platform, is described as the “world’s first Interoperable Blockchain Game universe” and sci-fi adventure. It’s built on Ethereum, so you can use ETH and NFTs for transactions such as purchasing accessories for your avatar.
- Roblox allows users to generate 3D worlds; play with other people using computers, mobile devices, Xbox One or VR headsets; and customize their avatars.
- The ABBA Voyage virtual concert in London features a custom-built ABBA Arena to showcase the group as digital avatars. Fans can buy different types of seats – auditorium, dance floor, dance booths and accessible seats. As of this writing, cryptocurrency is not accepted for payment.
- The Universal Studios Hollywood theme park has opened Mario Kart™: Bowser’s Challenge, a 3D/4D ride through underwater courses and cloud courses.
- Decentraland, the first virtual world owned by its users, provides environments such as a space adventure and medieval dungeon. The marketplace features land, wearables, emotes and more, which can be purchased with Ethereum MANA. A pink neonsaber, anyone?
As metaverse technologies mature and become more connected, an apt description for future immersive experiences may be that they are “going boldly where no man has gone before.”
A Sneak Peek Into the Metaverse of the Future
What are the experts saying? Industry analyst firms are tracking and sizing the metaverse market. In August 2022, McKinsey said that year to date, “more than $120 billion has flowed into the metaverse”…and that the metaverse has the potential to generate up to $5 trillion in value by 2030.2
Deloitte places the metaverse and Web3 in the fifth of six stages in the evolution of digital interaction. The sixth stage is spatial web, which links people, spaces and assets3 – more about spatial computing below. Pew Research begins an article on the metaverse in 2040 with “Hype? Hope? Hell? Maybe all three.” Survey responses are split as to whether the metaverse will (54%) or will not (46%) be a much-more-refined and truly fully immersive, well-functioning aspect of daily life for a half billion or more people globally.4
The metaverse reflects a shift from the internet of things to the internet of value.7
Gartner predicts that 25% of people will spend at least one hour a day in the metaverse by 2026 for work, shopping, education, social and/or entertainment.5 XR Today, self-described as “your essential resource for extended reality industry news and insights,” says that novel technologies based on user psychology will deepen user engagement – specifically, understanding that the human brain accepts both virtual and physical reality. Future immersive experiences will deepen emotional impact and realism.6
Despite speculation, uncertainty, lack of standardization and lack of governance, to name a few metaverse considerations, M&E enterprises are seizing an opportunity.
Tech Innovation, the Driving Force of Metaverse Growth
Tech innovation, backed by continuing investment and social acceptance, may be the main factor in metaverse growth. Adoption doesn’t seem to be an issue. Let’s touch on a few technologies.
Extended reality (XR) encompasses VR, AR and mixed reality (MR), a blend of VR and AR. VR and AR headsets have been around for quite a while. Some experts believe that VR headsets provide the best 3D immersive experiences for gaming, but they are typically big and heavy. Rich metaverse experiences call for XR headsets that are lighter and allow mobility. XR headsets are already on the market but expect new products that will improve design and functionality.
AI, and now generative AI, will broadly be involved with metaverse development despite ongoing concerns about privacy, transparency and ethics. As AI progresses, it enables more realistic, dynamic virtual game worlds and more realistic avatars whose expressions and actions mimic user behavior more accurately. AI and language processing support digital twins that entertain or educate global audiences in their native languages.
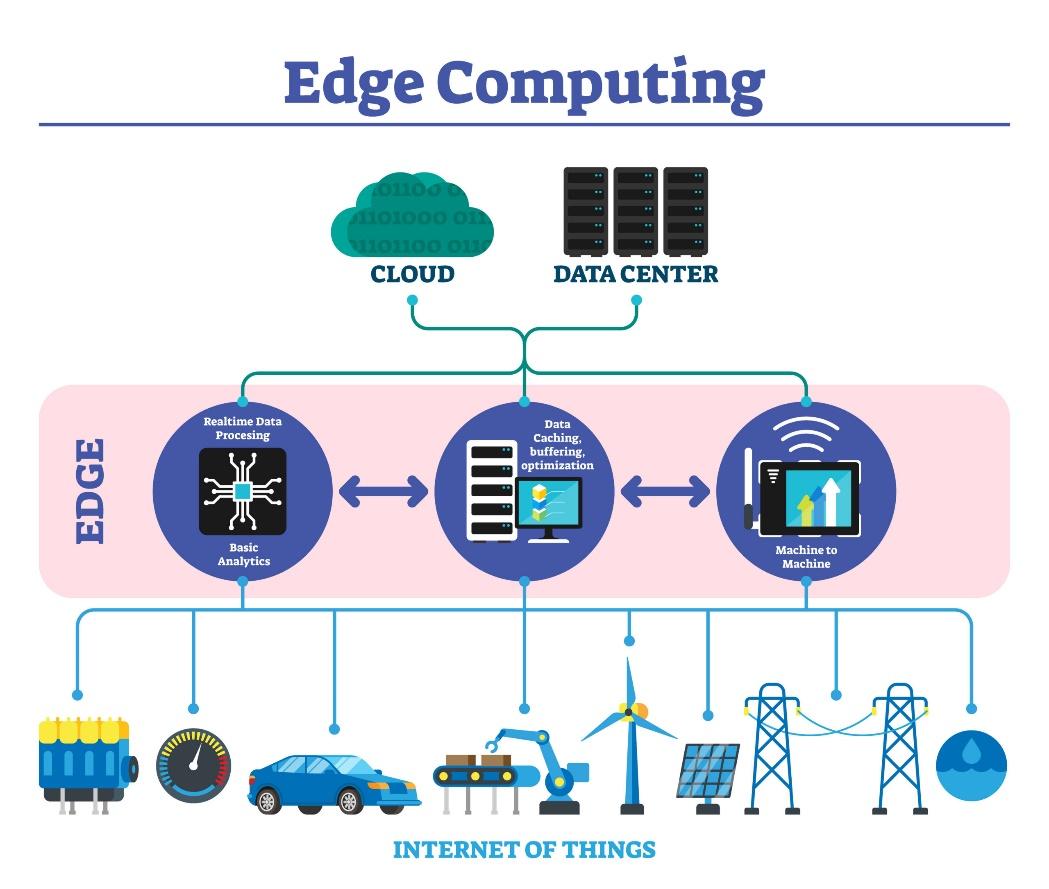
IoT devices and sensors are becoming more sophisticated. The data they collect moves to applications in which AI can process the data and improve elements of the metaverse. The greater availability of edge computing will speed data transport and support seamless immersive experiences with super-low latency.
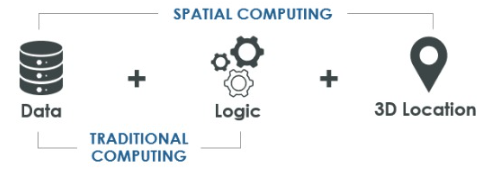
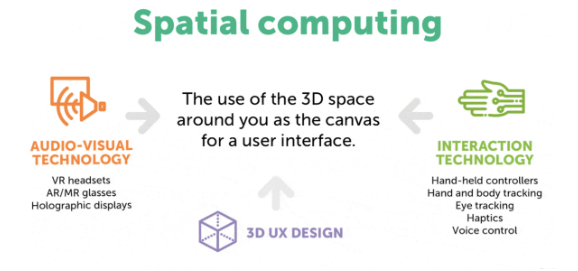
Spatial computing encompasses technologies (IoT, digital twins, AR, VR, etc.) that interact with 3D data. Spatial computing can overlay or integrate digital content with aspects of the physical world. An example is a game you can play with the backdrop of your real-world surroundings. Characters in the game can detect physical objects like a sofa and interact with it. Eyes, hands, bodies and voices control interactions in both virtual and physical worlds simultaneously in real time.8 As spatial computing advances, look for enriched user experiences and connected metaverse environments.
Whatever benchmarks you want to use – let’s say the first Star Wars movie to now – tech innovation is driving big changes in M&E.
The Metaverse Needs Infrastructure That Delivers Oscar-Worthy Performance
If infrastructure performance isn’t up to par, user experience suffers. Subpar performance makes it difficult for M&E enterprises to monetize digital assets, reduce costs and retain customers. Considering the substantial investments being made in the metaverse, infrastructure planning is a priority.
To achieve near-zero latency, the infrastructure must be capable of certain data-handling and transport capabilities. These are listed in our blog, What Is the Metaverse?. Additionally, explore the following topics with prospective data center providers:
- A private network and private cloud versus public clouds accessed via the internet
- Fast data transfer via direct onramps to public clouds
- Interconnection’s role in moving assets among data centers, CDNs, cloud and edge computing
- A software-defined platform such as the Open Cloud Exchange®, which enables digital media companies to streamline and orchestrate workflows
- Workloads distributed according to access requirements
- On-demand increase of bandwidth, storage and compute capacity
- Physical security measures and how cybersecurity is built into the tech stack
- The digital supply chain ecosystem of network, cloud and IT service providers with which you can collaborate

Write a New Script for M&E Digital Transformation
No one really knows how the development of the metaverse will unfold. Yet the combination of tech innovation and industry analyst predictions point to a flourishing metaverse. Progress will depend on how core metaverse technologies, including data center infrastructure, mature and interoperate.
Is your M&E enterprise ready for the future? Emerging tech has ups and downs – all the more reason to understand how colocation fits into your hybrid IT strategy. The right provider can smooth out transformation bumps and speed your journey.
To learn more about leveraging network, cloud, digital platforms and data centers to achieve your metaverse objectives, read the Media and Entertainment Industry Trends white paper.