Private AI: The Smart Choice for Many Enterprises
One of the great things about ChatGPT is that it’s publicly available and free to use. The problem is, anywhere between six and eleven percent of what’s fed into it can be sensitive data.1
With AI use booming, working smarter now includes remembering that everything you upload into open-source artificial intelligence platforms such as Perplexity, Copilot, Meta AI and the aforementioned ChatGPT is data that’s available to the rest of the world.
AI has been enthusiastically embraced as a transformative, must-have class of technology solutions. The urgency to integrate AI, however, has sometimes compelled developers to use open-source services, which can put data at risk. That urgency is warranted. A report by Accenture, Reinventing Enterprise Operations with Gen AI, states that “the number of companies that have fully modernized, AI-led processes has nearly doubled from 9% in 2023 to 16% in 2024. Compared to peers, these organizations achieve 2.5x higher revenue growth, 2.4x greater productivity and 3.3x greater success at scaling generative AI use cases.”2
What is Private AI and How is It Different From Public AI?
Businesses and other organizations are rushing to leverage the exciting and powerful capabilities offered by the plethora of generative AI products.
It’s not a question of whether to adopt AI, but how in order to reap the greatest advantage for their organizations.
Which brings us to the matter of articulating the differences between Public AI and Private AI and example use cases for each.
Private AI
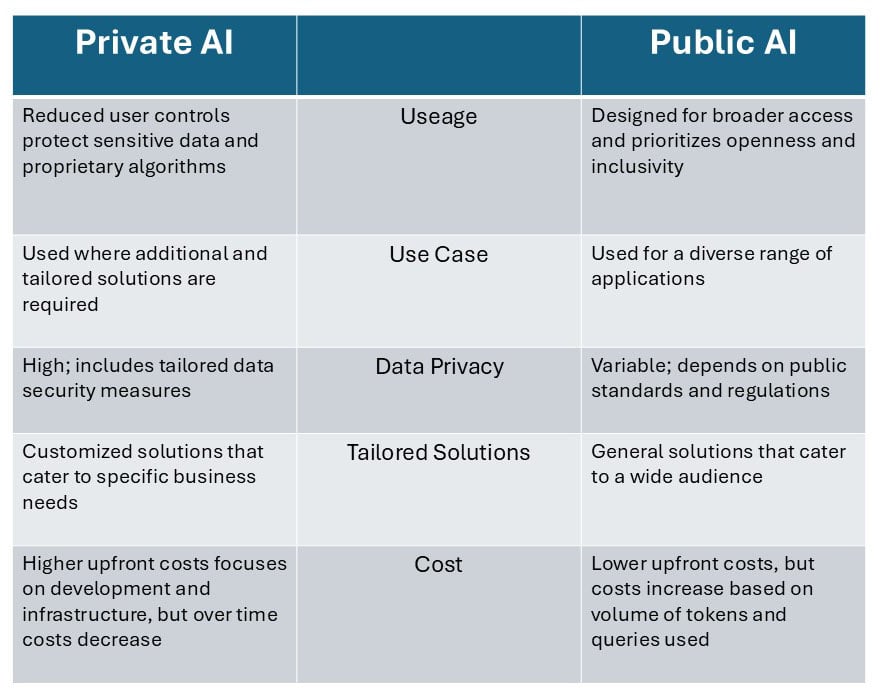
Private AI solutions are AI systems that are tailored to the specific business objectives and requirements of each organization. They operate in tightly restricted and secured environments that are owned and operated by organizations themselves, or deployed in third-party colocation data centers that deliver the power density, interconnection and reliability needed to support the workload and data transport requirements.
Private AI systems are trained on proprietary data and information, use organization-specific algorithms and models, and are carefully developed to ensure only explicitly authorized and monitored access to the AI systems. Data privacy and intellectual property protection are chief concerns, and compliance with regulatory standards such as HIPAA, GDPR, CPRA, the U.S. Privacy Act of 1974 and other regulations are monitored for adherence.
Private AI offers clear and compelling benefits to industries such as healthcare, finance, government and defense, where data protection is absolutely essential. But as data protection and ready-to-run, specialized features and functionality for other industry sectors become more vital, we’re seeing Private AI deployed more broadly.
Public AI
Public AI models and applications are designed to be widely accessible to a broad, general audience through open platforms, APIs and/or cloud service providers. Some commentators have characterized this as a democratized approach to AI, enabling access to and use of AI solutions by all types of users to increase their capabilities and productivity across a broad, unrestricted spectrum of business, personal, creative, entertainment and other use cases.
Public AI solutions have been trained on a variety of content types found in the public domain including company and personal websites as well as publicly available text, audio and visual news sources, periodicals, books, open records such as those held in the U.S. Library of Congress, and more.
Public AI solutions, with their machine learning libraries and pre-trained models, are understood to be open to the general public to address a broad range of tasks. By availing themselves of the various tools’ pre-trained models by way of familiar, user-friendly platforms, businesses, independent developers and “the average Joe” can leverage AI capabilities without substantial investments.
Additionally, Public AI generally, but not always meticulously, relies on voluntary adherence to public security standards and current regulations.
The Advantages of Private AI
With those considerations in mind, numerous organizations are now looking to Private AI, trained on proprietary content and organization-specific datasets to ensure:
- Data privacy and protection mandated by various government statutes or subject to industry regulations and standards
- Solution customization tailored to an organization's unique business missions, objectives and audiences
- Intellectual property protection as they leverage AI products and services to gain or grow their competitive edge
- Customer confidence that sensitive information is not accessible to unauthorized parties
- Increased revenue
We’ve seen this dynamic play out before as earlier technologies were first introduced in generic form, followed by organizations customizing and deploying them in secure environments, driven by similar concerns about data privacy, regulatory compliance, protection of their intellectual property, as well as operational expenses. A somewhat recent example of this has been the trend among organizations to migrate some or all of their IT operations from public to private cloud infrastructures.
Now that over 2,000 generative AI tools have been set loose in the global marketplace,3 developers, solution vendors, business executives, attorneys, legislators and others have turned their attention to developing rules of the road for using these tools responsibly.
Where You Deploy Your AI Solutions Matters
Reaching the artificial intelligence potential for your business depends on an infrastructure capable of high-density power, high-performance compute, direct cloud connections and digital ecosystem interconnection.
Just as many organizations have opted to deploy or migrate their IT assets from on-premises data centers or public cloud to data center colocation facilities, so too are they choosing to host their enterprise AI and machine learning models (both private and public) in colocation data centers.
CoreSite data centers are hubs for interconnection, serving as a broad and efficient funnel for data moved to train AI models and make inferences. In CoreSite’s colocation centers, enterprises can operationalize AI technologies leveraging power, cooling (including liquid cooling) and low-latency networks to support unique use cases, from the cloud to the edge.
CoreSite is also certified as part of the NVIDIA DGXTM-Ready Data Center Partner program, based on our ability to host scalable, high-performance infrastructure for organizations looking to capitalize on rising demand for artificial intelligence, machine learning and other high-density applications.
Know More
To learn more about the benefits of hosting your AI solutions in a CoreSite data center, visit the Artificial Intelligence Solutions area of our website or contact us.
References
1. Cyberhaven, 11% of data employees paste into ChatGPT is sensitive (source)2. Accenture, Reinventing Enterprise Operations with Gen AI (source)
3. AI Smart, How Many Generative AI Tools Are There? Key Insights (source)