Supporting Remote Work with Colocation
When COVID-19 burst onto the scene in March 2020, IT departments raced to provide a suddenly distributed workforce with the necessary resources to perform their jobs from outside the office. Today, as the dust settles, organizations are evaluating if a remote work environment will remain part of their IT strategies for the long term.
Remote work opportunities offer some key benefits to organizations and their employees. According to a report from Global Workplace Analytics, organizations that allow employees to telecommute half-time can save an average of $11,000 per employee, per year.
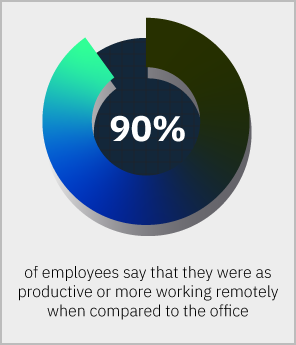
The benefits of a remote workforce reach beyond dollars. Without geographic hiring boundaries, organizations can access a wider talent pool. There is also evidence of improved or stable productivity – a statement 90% of employees in a survey by Owl Labs (State of Remote Work 2021).
However, permanently supporting a remote work landscape, requires a highly available and secure IT infrastructure that enables workers to safely access the data and applications they need, when they need it.
The necessary level of uptime and security can be difficult to achieve with an on-premises solution. A reduced on-site staff can enable unauthorized access to physical servers and the network simply because less people are in the office to deter this activity. A distributed workforce can also expose organizations to other security issues based on how employees connect to the corporate environment.
Cloud deployments have their own issues as even leading cloud providers only guarantee around 99.99% uptime. Even this minimal downtime can impact productivity and the bottom line.
Colocation Enables a Highly Available, Secure Flexible Workspace Environment
To be effective, a remote work IT strategy must safeguard the IT infrastructure and data, while ensuring uncompromising uptime. Modern third-party data centers are purposely designed to deliver these capabilities, while offering secure cloud connectivity.
Delivering Reliable Uptime
A reliable IT environment is essential to minimize downtime and data loss. Third-party data centers deliver the necessary reliability through a series of physical measures and best practices, and they back their services with a 100% SLA uptime guarantee.
Redundancies. Colocation facilities offer a series of redundancies to promote resiliency. Leveraging redundant critical systems – such as UPSes, generators, and mechanical equipment –data centers ensure continuation of services upon failure of equipment as well as concurrent maintainability of systems to provide uninterrupted operations. They also utilize multiple power paths and connectivity feeds to further eliminate single points of failure. Additionally, the diverse connectivity options within a third-party facility allow organizations to build network strategies that support ongoing availability, if one carrier falters.
Dedicated Teams and Best Practices. Colocation data centers also adhere to robust maintenance programs and equipment refreshes that are managed and executed by skilled technicians. By continually monitoring equipment and the network, the data center team can quickly address issues before they can threaten the stability of operations. Internal IT teams often put these routine practices on the back burner to focus on more core business IT initiatives. This can lead to downtime as equipment that has not been properly maintained has a greater chance of failing. Furthermore, unqualified and unskilled data center operators can do more harm than good within a data center.
Disaster Recovery. Third-party data centers can also support business continuity by helping organizations build disaster recovery (DR) solutions that utilize the provider’s geographically diverse data centers or disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS). Providers can also help organizations protect their data by implementing and managing backup solutions that align with their unique needs and their budgets.
Scalable Infrastructure. To support the influx of network traffic created by a remote workforce, colocation allows organizations to quickly and seamlessly scale network capacity. It also offers the agility to quickly add interconnections to support business growth and accommodate future demands. Also, organizations can quickly expand their space—as well as the requisite power and cooling—to ensure ongoing performance and reliability as the organization grows. Achieving this level of scalability internally can be time-consuming and complex.
Ensuring Security
A distributed workforce introduces a series of vulnerabilities that do not exist with traditional, onsite work conditions. When employees connect to the corporate environment through the public internet or other unsecured networks using endpoint devices without the appropriate security controls and patches, they expose the organization to cyberattacks. Organizations must establish new policies and physical controls to better manage these risks. Colocation has these measures in place.
Physical Security and Best Practices. Third-party data centers utilize robust physical and logical security measures, including perimeter fencing, 24x7x365 monitoring, onsite security personnel, biometric access controls and video surveillance cameras to fortify the environment. Their teams of on-staff security experts also ensure that security best practices, including emergency response, access control management, and third-party compliance requirements are precisely followed. The colocation team also monitors the threat landscape to stay abreast of emerging risks and implements leading-edge solutions to mitigate these issues.
Colocation facilities also participate in compliance validation programs to ensure their facilities adhere to the necessary regulations and standards. Organizations can leverage the data center’s compliance to help meet their own regulatory requirements.
Mitigating Cyberthreats. The remote work environment greatly increases the risk of a cyberattack, as internal IT teams have less control over the devices and connections employees use to log on to the corporate network. Third-party data centers can help organizations access the services necessary to combat cyberthreats and other vulnerabilities through either existing partnerships or the data center’s ecosystem of providers. This streamlined access is particularly critical to defend against distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, achieve zero-trust network access or address another concern that supports an organization’s own cybersecurity efforts.
Providing Cloud Access
While a fully cloud-based deployment cannot offer the same level of availability as best-in-class colocation services, cloud services remain an important element of a remote work landscape. Data centers with native onramps to leading cloud providers such as AWS, Google Cloud and Azure offer organizations the best of both worlds. Colocation can support a multi-cloud strategy by enabling organizations to tap into the specific services they need from various cloud providers. This flexibility helps organizations meet evolving business requirements, while also reducing egress costs.
CoreSite Delivers World-class Colocation to Support Flexible Workspaces
CoreSite offers a portfolio of 24 data centers equipped to support distributed workforces. With built-in system and network redundancies, robust security and compliance programs, and professional teams dedicated to optimizing facility operations, CoreSite protects the integrity of its customers’ data and operations.
In addition, the CoreSite Open Cloud Exchange® (OCX) provides enterprise-class connectivity services that simplify building and managing multi-cloud and networking solutions. Using OCX, customers can establish direct, secure and virtual connections to public clouds including AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Oracle and Alibaba. CoreSite’s high-performance network connections also offer guaranteed throughput and lower latency than public internet connections to improve the user experience. Organizations can directly manage these connections in near real-time using MyCoreSite, a software-defined service delivery platform.
CoreSite’s marketplace ecosystem also offers access to a continually growing community of partners and providers. Organizations can create relationships with these with businesses to address specific needs, including DDoS mitigation through Zayo and zero-trust networking with Seceon.
As businesses continue to integrate remote work environments into their forward-looking digital IT strategies, modern colocation providers like CoreSite can support the operational integrity and security of a flexible workplace solution to allow employees to remain productive and allow the business to pivot with changing demands.