Top 10 U.S. Data Center Markets and Why They Are Hot
Choosing where to house IT infrastructure is a key concern for enterprises, and with more than 2,700 U.S. data centers to choose from, IT leaders have a lot of options. While proximity to a corporate headquarters or concentration of customers and partners is a driving factor, several other considerations – including connectivity options, latency requirements, financial incentives, power cost and availability, environmental hazards and the business ecosystem within the region – impact the choice.
As businesses, government entities and individual users continue to consume growing quantities of cloud and IT services, aligning business needs and objectives with the available services and inherent value of specific data center locations will continue to influence decision-making and overall market demand.
Let’s take a look at 10 top data center markets and why they are hot.
1. Northern Virginia
Boasting more than 250 data centers, Northern Virginia (NOVA) is widely recognized as the data center capital of the world – for good reason. Located near Washington, D.C., the region offers access to the dense and diverse fiber cabling in the nation’s capital. This robust connectivity attracts prominent and rapidly growing enterprises as well as hyperscalers and their customers and partners. To support growing demand for data center services in the area, the region continues to invest in its network connectivity and power supply. In fact, a recent report predicts Northern Virginia will be the world’s first two-gigawatt data center market. For some context, NOVA is five times larger than the next largest market (Dallas), and larger than the six closest (in terms of number of data centers) markets combined.1
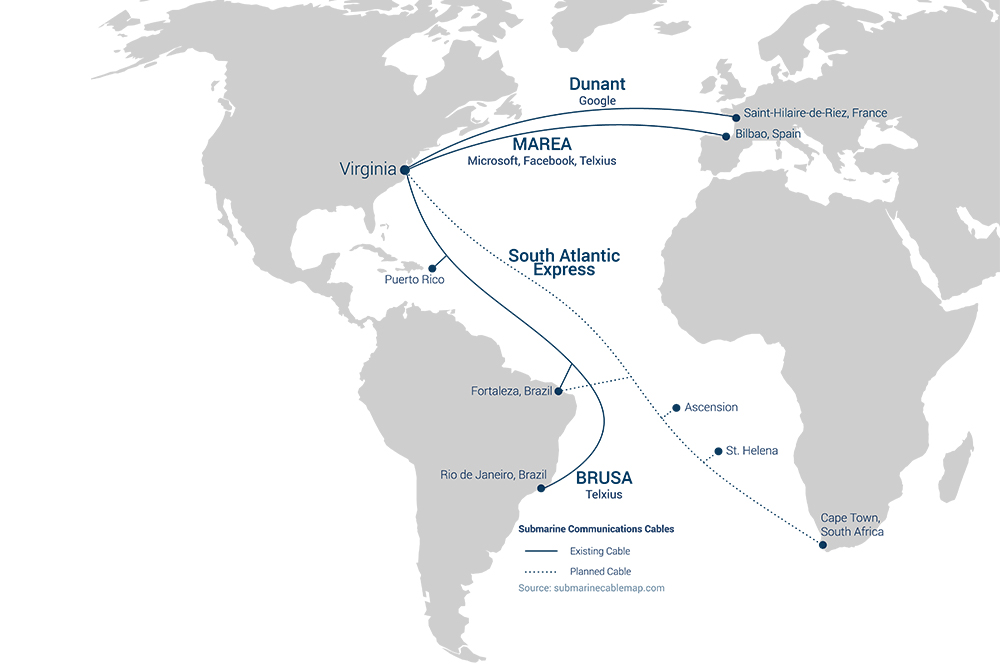
Northern Virginia’s central location allows enterprises along the Eastern Seaboard to share data with low latency. Its proximity to subsea cabling in Virginia Beach and the mid-Atlantic region creates access to global destinations. A few miles inland, it also is not in the path of hurricanes that threaten cities along the coast, providing a more stable operating environment.
The economic landscape of Northern Virginia is also enticing, offering the lowest commercial electricity rate in the mid-Atlantic region as well as generous tax incentives for data center providers and their tenants that meet specific spend and hiring criteria. Additionally, Loudoun County offers a 6% sales and use tax exemption on data center equipment.
2. Dallas
Located between two of the largest data center markets in the U.S. – Northern Virginia and Silicon Valley – Dallas features more than 150 data centers. Its central location, complemented by the lowest real estate costs in primary U.S. data center markets and power costs well below the national average, make it attractive to businesses. Add metro and long-haul connectivity as well as a strong economy to the mix and Dallas offers a sound, affordable alternative to higher-priced West Coast data centers.
3. Silicon Valley
Lauded as a hub of innovation, Silicon Valley is home to industry giants such as Google, IBM, Microsoft, Sony and Amazon. Despite having some of the highest real estate and power costs in the country, Silicon Valley remains a major data center market, touting nearly 150 facilities.
Demand in Silicon Valley is largely due to its robust connectivity options, including onramps to leading cloud providers, internet exchange points (IXPs) and high-capacity fiber networking. This robust connectivity makes the area one of the most interconnected locations in the world and a key connectivity point for the West Coast.
4. Los Angeles
Like Silicon Valley, Los Angeles has a high cost of doing business that drives some enterprises to other markets. However, the city’s large and continually growing population continues to increase demand for data center services, helping the city retain its status as a top data center market. LA is also a hub for entertainment, manufacturing and international trade, thanks to its sophisticated network fabric, abundance of fiber connectivity and the presence of One Wilshire, one of the most interconnected buildings in the U.S. – and where CoreSite’s LA1 Data Center is located.
While building more data centers in this area is slow because of exorbitant real estate and operating costs and a lack of available space, existing data centers continue to thrive.
5. New York Tri-State Area
As the epicenter of the financial services industry in the U.S., New York City is a major global destination for businesses. While many organizations require a data center presence within the city to achieve ultra-low latency connections, those without such intense demands can leverage any of the 130+ data centers in the surrounding tri-state area of New York, New Jersey and Connecticut. These locations offer geographic proximity to New York City at lower cost and provide greater availability of space for data center expansion. The tri-state area also offers access to transatlantic cabling and fiber connectivity without the high operating costs of the city. The region is also at low risk for natural disasters, further bolstering operational integrity and uptime.
6. Chicago
Centrally located between the East and West Coasts, Chicago offers more than 120 data centers. Ranking as one of the top five cities in the country for connectivity, the city runs its fiber optic cabling along railroad tracks that connect the coasts and is also home to one of the largest peering exchanges in the country, helping Chicago serve as a connectivity gateway to the global market.
In addition to power costs below the national average, Chicago offers reliable energy delivery through an almost entirely underground power infrastructure that offers protection from unstable weather conditions and other unanticipated events. Chicago’s cost of living is also significantly lower than that in other major cities such as New York City and San Francisco, helping attract a highly skilled workforce that lures large enterprises such as Google, Salesforce and Uber. Additional financial benefits include Illinois 10.25% tax incentives that exempt data center providers and their tenants from state and local sales tax on data center equipment purchases and a colder climate that helps minimize cooling costs. The city also has a low propensity for natural disasters, and Lake Michigan offers a ready and affordable supply of water to support data center cooling.
7. Washington, D.C.
As one of the most highly interconnected regions in the U.S., it is no surprise that the nation’s capital is home to almost 100 data centers. Despite the area’s high costs, businesses embrace the area for its rich networking, heavy concentration of fiber networks and low-latency access to government agencies and global powerhouses that operate within the district.
8. Atlanta
With the third-largest concentration of Fortune 500 companies in the U.S., Atlanta is one of the fastest-growing data center markets in the country. Its more than 70 data centers host prosperous technology, health, digital media, transportation and security companies, as well as industry giants such as Coca-Cola, Delta Airlines, UPS, Georgia-Pacific and Cox Enterprises.
Atlanta’s advantages include competitive energy costs, a robust transportation infrastructure, strong fiber connectivity and a skilled workforce. The metro area is also at low risk for national disasters and offers a highly reputable and reliable power grid that provides businesses with peace of mind around service delivery.
9. Miami
Located on the Florida peninsula, Miami is a gateway to Latin America, the Caribbean and Europe. Serving as a termination point for subsea cabling that connects the U.S. to South America, the city offers secure, ultra-low-latency connections to global markets and is also home to the Network Access Point (NAP) of the Americas (NOTA), one of the world’s largest connection points. These benefits have attracted major enterprises, particularly in the technology and financial services industries.
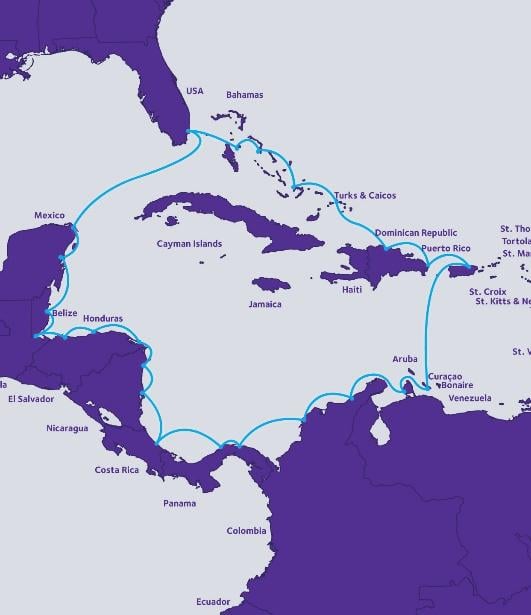
Miami’s transportation infrastructure, including Port Miami and Miami International Airport (MIA), adds to its competitive edge, allowing businesses and their supply chains to easily maneuver in the area. With no inventory or unitary taxes for businesses, a relatively low state corporate income tax, four foreign trade zones (FTZ) and reasonable energy costs, Miami offers financial advantages as well.
We offer even more reasons to deploy infrastructure in a recent blog: Why a Miami Data Center is Good for Business.
10. Phoenix
Offering lower taxes, affordable power and real estate, robust fiber and cable connectivity, and minimal exposure to natural disasters, Phoenix is another top data center locale. Businesses are choosing any of the city’s 60+ data centers over competing sites along the West Coast to serve the area. Arizona also offers a reliable power grid with access to renewable energy sources for businesses dedicated to sustainability efforts.
Want to see how CoreSite can help you access all these markets? First, check out our latest map of data center campus locations (which includes details on direct cloud onramp availability) and then learn about each market and global interconnection.